More commonly called just sperm, the spermatozoon (plural spermatozoa) is the male gamete and the smallest but most highly specialised cell in the body. Like eggs, sperm 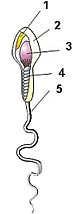 are haploid. They are carried from the man’s body in fluid called seminal fluid or semen. There are about 60 million sperm cells in 1 millilitre of seminal fluid, and the average volume of ejaculated semen is about 5mls. Sperm are produced continuously throughout the life of a man after puberty.
are haploid. They are carried from the man’s body in fluid called seminal fluid or semen. There are about 60 million sperm cells in 1 millilitre of seminal fluid, and the average volume of ejaculated semen is about 5mls. Sperm are produced continuously throughout the life of a man after puberty.
- acrosome – packet of proteolitic enzymes that help the sperm to get through the outer layers of the egg.
- sperm surface membrane
- haploid nucleus – contains the genetic material
- midpeice – contains tightly packed mitochondria to power the tail
- tail or flagellum – beats rapidly to propel the sperm through the female reproductive tract
 Development of the early embryo
Development of the early embryo

What's your opinion?
Average rating




Not yet rated